What Is Augmented Reality (AR)?
Ever wondered what’s the deal with Augmented Reality (AR)?
Why does everyone from tech giants to small businesses rave about it?
And most importantly… how does it actually work?
Today, I’m breaking it down. No fluff. No jargon overload.
Just the facts, the applications, and why you need to care.
Let’s dive in.
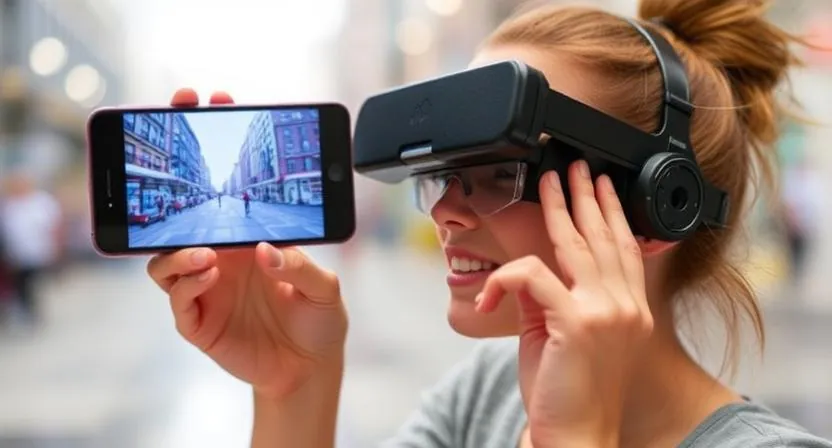

What Is Augmented Reality (AR)?
Augmented Reality (AR) is tech that overlays digital content onto the real world.
Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which throws you into a fully digital environment, AR keeps you in reality—just enhanced.
Think Snapchat filters. Pokémon GO. Google Lens.
You look through your phone or AR glasses, and boom—digital objects, information, or graphics appear right in front of you, blending with your surroundings.
How Does Augmented Reality Work?
It’s not magic (though it feels like it sometimes).
AR works by using:
- Cameras & Sensors: Detects surroundings, depth, and objects in real-time.
- Processing Power: Your phone, tablet, or AR glasses handle the computing.
- AI & Computer Vision: Recognizes objects and places digital elements in the right spot.
- Displays: Your screen (or AR glasses) projects the digital overlay.
It’s a mix of hardware + software + smart algorithms that make digital content interact with the real world seamlessly.
Types of Augmented Reality
Not all AR is built the same. Here are the main types:
1. Marker-Based AR (Image Recognition)
- Uses printed markers (QR codes, images, symbols) to trigger digital content.
- Example: Scan a magazine ad, and a 3D model pops up.
2. Markerless AR (Location-Based AR)
- Uses GPS, accelerometers, and other sensors to place AR objects without needing a marker.
- Example: Pokémon GO, where creatures appear in different locations.
3. Projection-Based AR
- Projects digital images directly onto real surfaces without needing a screen.
- Example: Holograms or smart projectors displaying interactive content.
4. Superimposition-Based AR
- Replaces or enhances parts of the real world with digital elements.
- Example: Google Translate’s AR mode, which swaps out foreign text with a translated version.
Real-World Uses of Augmented Reality
1. Gaming & Entertainment
- Pokémon GO made AR a household name.
- Snapchat & Instagram filters? AR at work.
- Apple’s ARKit & Google’s ARCore let developers create insane AR experiences.
2. Retail & Shopping
- Try on clothes, glasses, or makeup—without stepping into a store.
- IKEA lets you place furniture in your home before buying.
3. Healthcare & Medicine
- AR helps doctors visualize organs & veins during surgery.
- Medical students can practice procedures using AR simulations.
4. Education & Training
- Learn about planets by pointing your phone at the night sky.
- Mechanics, pilots, and even astronauts train with AR overlays.
5. Real Estate & Architecture
- Walk through a house before it’s even built.
- AR home tours let buyers explore spaces remotely.
6. Automotive & Navigation
- AR-powered GPS overlays directions onto your windshield.
- Mechanics use AR for repairs without flipping through manuals.
7. Marketing & Advertising
- Interactive AR billboards? Yep, those exist.
- Brands use AR to make packaging more engaging.
AR vs. VR: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | Augmented Reality (AR) | Virtual Reality (VR) |
|---|---|---|
| Real-world integration | ✅ Enhances real world | ❌ Fully immersive |
| Hardware required | Smartphones, AR glasses | VR headsets |
| Example | Pokémon GO, Snapchat filters | Oculus Rift, PlayStation VR |
| Use cases | Gaming, retail, healthcare | Gaming, training, simulation |
Both are powerful. But AR blends digital with reality, while VR replaces reality.
The Future of Augmented Reality
We’re only scratching the surface.
What’s next?
- AR Glasses: Apple Vision Pro, Meta’s AR glasses—no more staring at phone screens.
- 5G-powered AR: Faster, more immersive experiences.
- AI + AR: Smarter overlays, better personalization.
- AR in the Metaverse: A digital world merged with our own.
Soon, AR won’t just be a feature. It’ll be a part of daily life.
FAQs: Augmented Reality (AR)
Is AR the same as VR?
No. AR adds digital elements to the real world, while VR replaces it with a fully digital one.
What do I need to experience AR?
Most AR runs on a smartphone or tablet. For advanced experiences, AR glasses like HoloLens take it to the next level.
Is AR expensive?
Basic AR is free (think Instagram filters). Advanced AR (like custom business solutions) can get pricey.
Can AR be used without the internet?
Some AR apps work offline, but for real-time data and cloud-based AR, you’ll need an internet connection.
What industries will benefit most from AR?
Gaming, retail, education, healthcare, and real estate are leading the way—but honestly, AR can transform any industry.
Final Thoughts
So, what is Augmented Reality (AR)?
It’s the tech that blends the digital with the real world—and it’s here to stay.
From gaming and shopping to healthcare and training, AR is changing the way we live, work, and interact.
And we’re just getting started.